Essential Preparations to Elevate Patient Safety During Blood Draws
Thoroughly Confirm Patient Identity to Fortify Safety Measures
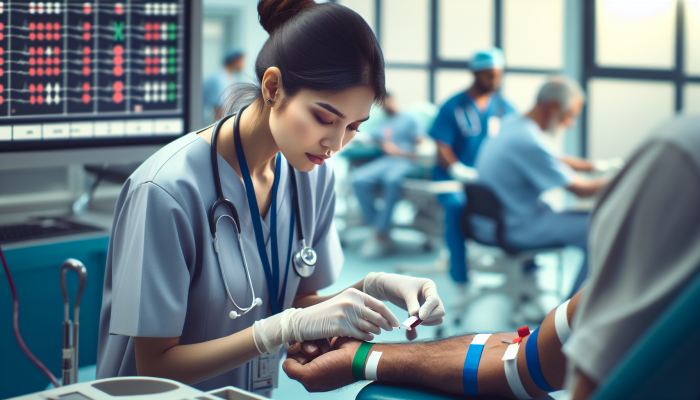

Every blood draw is an opportunity to significantly enhance patient safety, starting with meticulous identity verification. It is crucial to confirm the patient's identity utilizing at least two distinct identifiers, such as their name, date of birth, or medical record number. This essential practice helps prevent severe errors, ensuring that the right patient receives the appropriate treatment. Consider the potential dire outcomes of identity mix-ups, which can lead to misdiagnoses—a situation every healthcare professional aims to avoid, and one that is easily prevented through diligent verification.
Creating a culture of vigilance begins with these foundational checks. This process goes beyond mere procedure; it is a vital aspect of patient care that resonates throughout the healthcare continuum. Integrate this practice into your daily routine. Engaging in a brief dialogue with the patient not only reassures them but also confirms your readiness. Ask questions like, “Are you comfortable?” These moments spent on verification can turn a potentially chaotic procedure into a smooth experience, greatly reducing the chances of errors in healthcare.
Additionally, consider leveraging modern technology to aid in the identification process. Implementing barcode systems on wristbands and incorporating electronic health records can simplify this critical step, minimizing human error and enhancing operational efficiency. In a fast-paced healthcare setting where every second counts, adopting such technologies can substantially improve your practice while maintaining an unwavering commitment to patient safety.
Assemble All Required Equipment for a Seamless Blood Draw
Imagine the frustration of starting a blood draw only to realize that you’ve left out a crucial piece of equipment. Such oversights can pose serious risks to patient safety. Gathering all necessary materials before initiating the procedure is not merely recommended; it is essential. Ensure that sterile needles, collection tubes, alcohol swabs, and gauze are organized and readily available to facilitate a smooth process.
Before commencing the blood draw, take a moment to carefully inspect each item. Are all items sterile? Are the needles appropriately sized for the patient’s veins? Conducting a quick inventory can help in preventing unnecessary complications during the procedure. Establishing a state of preparedness and calm is essential, allowing both the practitioner and the patient to feel secure and assured throughout the entire process.
Consider creating a comprehensive checklist that encompasses every item needed for a successful blood draw. This tool can be especially beneficial in busy clinical environments. It’s not just about improving efficiency; it’s about ensuring that each blood draw complies with the highest safety standards. A well-prepared professional exudes confidence, and that assurance can significantly enhance the overall patient experience.
Select the Best Vein to Ensure Successful Blood Draw Results
Choosing the optimal vein is akin to selecting the ripest fruit from a tree—both require a discerning eye and a touch of finesse. Assessing the visibility and palpability of veins is crucial for achieving a successful and safe blood draw. The antecubital fossa, or the area inside the elbow, is often the preferred site; however, each patient presents unique anatomical features. Factors such as obesity, age, and hydration levels can complicate the vein selection process.
Skilled phlebotomists know that palpating the area to locate a vein is just as important as visual assessment. Gently feeling the area can help identify the most suitable vein. Is it elastic? Does it show a bounce-back response? These indicators suggest a viable candidate. If difficulties arise, don’t hesitate to explore alternative sites. The dorsal veins on the hand or even those in the forearm might offer more accessible options for certain patients.
Effective communication with your patient is equally important. Clearly explain what they can expect and reassure them that your aim is to provide a quick and painless experience. Building trust is essential in any medical scenario, and a calm patient is often more cooperative, paving the way for a smooth blood draw.
Ensuring Safety Throughout the Blood Draw Procedure

Utilize Proper Techniques for an Optimal Blood Draw Experience
Employing the correct technique is vital for minimizing discomfort and ensuring safety during blood draws. The method of needle insertion is fundamental; a forceful thrust can lead to pain and anxiety, while a gentle, deliberate approach fosters trust and cooperation. Position the needle at an angle between 15 and 30 degrees for optimal access, aiming to enter the vein while minimizing trauma.
While practice enhances proficiency, it’s crucial to remain vigilant throughout the procedure. Are you attentive to signs of discomfort? Is the patient exhibiting signs of anxiety? As you refine your technique, remember to adapt your approach to fit each patient’s unique needs. If they seem tense, take a moment to provide comfort. A touch of empathy can significantly improve the atmosphere, making the experience feel less intimidating for patients.
Additionally, never underestimate the power of distraction. Engaging the patient in light conversation or asking about their day can shift their focus away from the procedure. This simple yet effective strategy can turn a potentially nerve-wracking experience into a more relaxed one, thereby enhancing overall safety during the blood draw.
Continuously Assess Patient Comfort Throughout the Procedure
Monitoring patient comfort should be an intrinsic part of the blood draw process, not an afterthought. Continuously evaluating the patient's comfort can significantly influence the success of the procedure. Are they fidgeting? Do they appear pale or sweaty? Such signs warrant immediate attention. Vigilance extends beyond mere vital checks; it involves being sensitive to the patient’s emotional state.
Take the environment into account as well. Is the room too cold? Is the lighting adequate? Minor adjustments can dramatically improve comfort levels. Encourage patients to relax, breathe deeply, and stay calm. Your composed demeanor can serve as a calming influence, fostering a more conducive setting for a successful blood draw.
Informing patients about what to expect during the procedure is equally essential. Knowledge dispels fear. Clearly outline each step, from needle insertion to the sensations they might experience. This transparency alleviates anxiety and empowers the patient, making them an active participant in their care journey.
Adhere to Safe Sharps Handling Practices to Prevent Injuries
The significance of safe sharps handling cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental aspect of blood draw safety protocols designed to protect both the practitioner and the patient. Always dispose of needles immediately after use in designated sharps containers. This practice is not just a recommendation; it is a legal and ethical obligation. Improperly discarded needles can lead to severe injuries and potential infections—risks that must never be underestimated.
Before beginning the blood draw, ensure that the sharps container is within easy reach. Hesitation has no place in safe disposal practices. Regularly review safety protocols with your team; a well-informed staff is your strongest defense against accidents.
Moreover, consider implementing a comprehensive safety checklist that includes procedures for sharps handling. Regular drills can reinforce these practices, ensuring that all team members are aligned. The mantra should be clear: safety first, always.
Maintain Sterility During the Blood Draw Procedure for Maximum Safety
Upholding sterility acts as the shield that protects patients from infection. Every piece of equipment used, from the needle to the alcohol swab, must be sterile. Initiate the process by disinfecting the puncture site with an appropriate antiseptic solution—this is your first line of defense against microbial contamination.
Remain vigilant. Any lapse in sterility can lead to complications that jeopardize patient health. Ensure your hands are thoroughly washed and dried, and don sterile gloves throughout the procedure. Each step taken to maintain sterility is critical and requires focused attention.
Educate your staff on the vital importance of sterilization and its effective implementation. Regular training sessions can reinforce this knowledge, ensuring everyone understands how to maintain a clean environment. Remember, a sterile procedure is not merely about preventing infections; it also instills confidence in your patients.
Implementing Comprehensive Infection Control Measures
Prioritize Hand Hygiene as a Fundamental Infection Control Strategy
Hand hygiene is the unsung hero in the fight against infections. It’s astonishing how something as simple as proper handwashing can dramatically decrease the transmission of pathogens. Thorough handwashing is essential before and after each blood draw.
Utilize soap and water whenever possible, scrubbing for at least 20 seconds. Hand sanitizer can act as a valuable alternative in situations where soap and water are not available, but it should never replace the thoroughness of effective handwashing. Educate your team on proper techniques and the significance of this practice—consistent repetition fosters good habits.
Consider placing visual reminders near sinks or hand sanitizing stations. These cues can reinforce the importance of hand hygiene, prompting staff to pause and wash their hands properly. A workplace culture that prioritizes hygiene significantly mitigates the risk of infections.
Moreover, involve patients in this process. Encourage them to wash their hands before the procedure or use hand sanitizer. This collaborative approach ensures that everyone is aligned and aware of the crucial role hygiene plays in their care.
Utilize Sterile Gloves to Elevate Patient Protection and Safety
Wearing sterile gloves is essential not only for your protection but also as a safeguard for your patients. Each pair of gloves serves as a barrier that prevents the transfer of harmful microorganisms. Before putting on gloves, ensure your hands are clean and dry for optimal effectiveness.
Selecting the right glove size is critical. Ill-fitting gloves can hinder dexterity and increase the risk of accidental contamination during the procedure. Take a moment to inspect for any imperfections before use. A minor tear can turn a protective measure into a pathway for infection.
Beyond the technical aspects, foster a culture of accountability. Encourage your staff to view gloves as an integral part of their toolkit. Regular training sessions can reinforce this message, ensuring that everyone comprehends the importance of correctly and consistently wearing gloves throughout the blood draw process.
Furthermore, remind your team that gloves do not replace the necessity of hand hygiene. Even while wearing gloves, thorough handwashing remains imperative before and after procedures. Incorporate these practices into daily routines to elevate the standard of care in your practice.
Thoroughly Clean the Puncture Site to Effectively Prevent Infection
Cleaning the puncture site is one of the simplest yet most vital steps in preventing infection. Start by disinfecting the area with an alcohol swab or antiseptic wipe—this serves as your first line of defense against bacteria.
However, don’t just swipe and go; it’s crucial to allow the antiseptic to dry completely. This permits the disinfectant sufficient time to work effectively. Patience is key here. Rushing through this step can invite harmful pathogens into the bloodstream, posing serious risks to patient health.
Additionally, educate patients about the importance of this step. Explain why you are cleaning the area and what they can do post-procedure to maintain cleanliness. This will inform and empower them, fostering collaboration in their care.
Employing a systematic approach to site cleaning can streamline the process. Consider developing a checklist or protocol for every team member to follow to ensure consistency. This can significantly reduce the risk of infection and enhance the overall quality of care.
Ensure the Safe Disposal of Sharps to Protect Everyone Involved
The proper disposal of sharps is an absolute necessity in maintaining a safe healthcare environment. Always place used needles and other sharp instruments in designated sharps containers immediately after use. These containers should be puncture-resistant, leak-proof, and readily accessible to prevent accidents during disposal.
Make it a priority to educate your team about the importance of immediate disposal. A needle left lying around, even for a moment, presents a severe risk—not just to healthcare professionals but to everyone nearby. Regular training sessions can reinforce these protocols, ensuring that safety remains at the forefront of practice.
Moreover, consider implementing a “no-touch” policy for sharps disposal. This means that as soon as a needle is used, it should be placed directly into the sharps container without passing through another person’s hands. This approach reduces the chances of accidental needle sticks and reinforces a safety culture.
Keep the conversation about sharps disposal ongoing. Regular updates and reminders can keep this critical safety aspect fresh in everyone's mind, ensuring a collective commitment to safe practices.
Comprehensive Care After the Blood Draw Procedure
Apply Pressure to the Puncture Site for Effective Recovery
Applying pressure to the puncture site after needle removal is a crucial step that must never be overlooked. This straightforward action aids in stopping bleeding and reduces the likelihood of bruising. But why is this significant? Excessive bleeding can lead to complications and discomfort for the patient, possibly necessitating further medical interventions.
Utilize a sterile gauze pad to apply firm, consistent pressure for at least a few minutes. Instruct the patient not to lift the pressure until you provide the green light. This promotes clotting and ensures a smooth recovery. It’s a minor detail that can substantially enhance patient comfort and safety.
Moreover, educate patients on the importance of post-procedure care. Advise them to avoid strenuous activities for the rest of the day and provide clear instructions on when to seek medical attention. An informed patient is a safer patient, and this knowledge can transform their overall experience.
Lastly, consider the emotional aspect of aftercare. Some patients may feel light-headed or anxious post-procedure. Stay alert and attentive, ready to offer reassurance and support. Creating a calming environment fosters trust and significantly enhances the overall patient experience.
Closely Monitor for Potential Complications After the Blood Draw
Remaining vigilant for complications following a blood draw is of paramount importance. While most procedures occur without incident, complications can arise, such as excessive bleeding, bruising, or signs of infection. Vigilance in monitoring these indicators is essential for addressing any issues before they escalate into serious concerns.
Stay attentive and observant during the recovery period. If a patient seems pale or dizzy, check their blood pressure and ensure they are adequately hydrated. Conduct a quick assessment and provide any necessary interventions. Empower your team to notice and act on these observations—every second counts when it comes to patient safety.
Inform your patients about what to look for post-procedure. Signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge, should prompt immediate medical attention. Knowledge empowers patients and can significantly reduce the likelihood of complications going unnoticed.
Additionally, cultivate a culture of open communication. Encourage patients to voice their concerns or questions during the recovery period. This open dialogue fosters trust and ensures everyone feels supported throughout the process.
Deliver Clear and Concise Patient Instructions for Post-Procedure Care
Providing clear and concise post-procedure instructions is vital for patient safety and satisfaction. After a blood draw, patients should thoroughly understand how to care for the puncture site and when to seek medical attention. Supplying a printed handout can serve as an invaluable reference, minimizing the likelihood of misunderstandings.
Encourage patients to keep the site clean and dry for at least 24 hours. Inform them to avoid hot baths, swimming pools, and strenuous exercise during this recovery period. These straightforward guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of infection and promote faster healing.
Furthermore, explain the signs of potential complications—such as excessive bleeding, increased pain, or indications of infection—and advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they notice any of these issues. Empowering patients with this knowledge instills a sense of control and confidence in their care.
Lastly, consider scheduling a follow-up appointment if necessary. This gesture demonstrates that you care about their well-being and allows you to address any lingering questions or concerns. Follow-up care is crucial to the blood draw process, extending your commitment to patient safety beyond the immediate procedure.
Best Practices for the Safe Disposal of Medical Materials
Ensure the Safe Disposal of Sharps to Safeguard Health
The proper disposal of sharps is an absolute requirement in the medical field. Used needles, syringes, and lancets must be placed in designated sharps containers immediately after use. These containers should be puncture-resistant, leak-proof, and easily accessible. Every healthcare professional must understand that the risk of needlestick injuries (NSIs) is real and significant.
Educate your team on the importance of immediate disposal. A needle left lying around is a severe accident waiting to happen. Regular training sessions can ensure that everyone is well-versed in the correct protocols for sharps disposal, fostering a culture of safety that permeates your practice.
Additionally, a system should be implemented to monitor sharp containers. Regularly check them to ensure they are not overflowing and are disposed of according to local regulations. This practice maintains a safe environment while demonstrating a commitment to best practices in patient care.
Lastly, encourage open dialogue among the team regarding sharps safety. Regular discussions can highlight the importance of vigilant disposal practices and invite everyone to share their experiences and suggestions for improvements.
Handle Biohazardous Waste with Extreme Care and Precision
Disposing of biohazardous waste is a serious matter that requires meticulous attention. Blood-soaked materials, such as gauze or collection tubes, must be placed in designated biohazard bags. These bags should be marked and sealed to prevent leaks, protecting staff and patients from potential hazards.
Ensure that everyone is adequately trained to identify and dispose of biohazardous materials in your practice correctly. Regular training updates can keep this information relevant and impactful. Consider implementing a labeling system that indicates which materials should be treated as biohazardous, further reducing the risk of mishandling.
Moreover, stay informed about local regulations surrounding the disposal of biohazardous waste. Compliance is not just a legal obligation; it's a foundational step in maintaining a safe healthcare environment. Neglecting to follow these regulations can lead to serious consequences, including financial penalties and damage to your practice’s reputation.
Foster a culture of accountability where staff members feel empowered to report any potential lapses in biohazardous waste management. This open communication can strengthen teamwork and ensure that everyone is committed to maintaining safety and compliance.
Comply with Local Regulations for Effective Medical Waste Disposal
Understanding and adhering to local regulations concerning medical waste disposal is essential. Laws governing medical waste disposal vary significantly from region to region, making it crucial to stay informed and compliant. Noncompliance can result in fines, legal action, and reputational damage to your practice.
Regularly review local guidelines and ensure your staff is trained on these regulations. Establish a clear protocol for disposal practices that aligns with these rules. A well-documented process can serve as a reliable reference for every team member, instilling confidence in their compliance practices.
Additionally, consider conducting periodic audits of your waste disposal procedures. This proactive approach can help identify areas needing improvement and ensure everyone adheres to established protocols. An audit serves not only as a compliance check but also as an opportunity to highlight and celebrate best practices within your team.
Cultivating a culture of regulatory awareness can transform how your team approaches waste disposal. Encourage team discussions regarding compliance, soliciting suggestions and feedback on improving practices. This collaborative approach enhances safety and fosters a stronger sense of camaraderie within your team.
Commitment to Ongoing Training and Improvement in Blood Draw Techniques
Stay Current on the Latest Best Practices in Blood Draw Safety
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, it is vital to remain updated on the latest guidelines and techniques for safe blood draws. The medical field is constantly advancing, influenced by new research, technology, and evolving best practices. A commitment to lifelong learning is not merely a professional obligation; it enhances patient safety and the quality of care.
Encourage all team members to participate actively in regular training sessions. Consider establishing a monthly learning forum where staff can share insights, discuss recent developments, and review procedures. This environment of continuous improvement allows everyone to contribute to evolving practices.
Moreover, subscribe to industry newsletters or join professional organizations that provide blood draw safety resources. These platforms can offer invaluable information on the latest research, emerging technologies, and innovative practices that enhance patient safety.
Finally, the organization should encourage staff to attend workshops and conferences













